Neuroimmnomodulation effect of acupuncture
Our research work focuses on the clinical and laboratory practice of acupuncture therapy for surgical stress induced immune disturbance and the mechanisms underlying the regulatory effect of acupuncture.
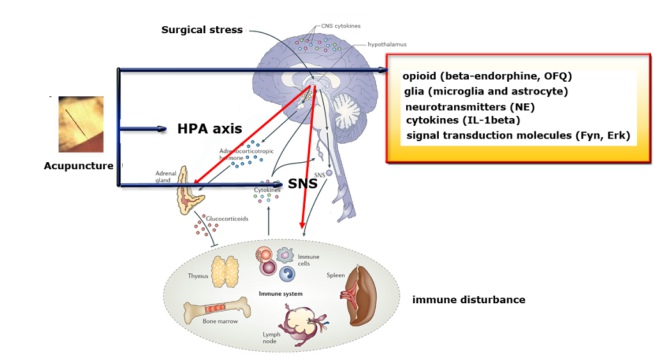
The acupuncture induced output signal has been observed to correct the dysfunction of immune system and induce a homeostatic effect on the body through the accommodation of nervous and immune systems. The sequential electrical stimulation applied to certain acupoint, such as the Zusanli acupoint (ST 36), was favorably effective in the treatment of surgery-induced immunodeficiency and physical disorders. The hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal (HPA) axis and sympathetic nervous systems (SNS) were involved in the regulatory effect of acupuncture on post-surgery immune disturbance. At the molecular level, the acupuncture induced neuroimmune regulation is mediated through multiple pathways and involves various bioactive molecules including steroids (corticosteroid), neuropeptides (endogenous opioids, such as beta-endorphin, nociceptin/orphanin FQ, N/OFQ), cytokines (IL-1beta), neurotransmitters (noradrenalin) and signal transduction molecules (Fyn, Erk), which form the basis for bidirectional coordinated neuroimmune regulation in response to homeostasis disturbances. An integrated investigation including the approaches of molecular biology, integrative physiology, and clinical research is considered to further improve the understanding of the acupuncture-mediated regulation of neuroimmune function, and eventually lead to better applications of acupuncture for the treatment of immune-related diseases.
Main subject:
Neuroimmnomodulation effect of acupuncture and opioids & opioid receptor
Neuroimmnomodulation effect of acupuncture and microglia activation
Neuroimmnomodulation effect of acupuncture and signal transduction molecules
Publications:
1. Jun Wang, Hui Zhao, Qi-Liang Mao-Ying, Xiao-Ding Cao, Yan-Qing Wang, Gen-Cheng Wu. Electroacupuncture downregulates TLR2/4 and pro-inflammatory cytokine expression after surgical trauma stress without adrenal glands involvement. Brain Research Bulletin, 2009, 80(1-2):89-94.
2. S Xiao, J Wang, JW Jiang, XD Cao, GC Wu, H Zhao. Characterization of Fyn Signaling On The Age-Dependent Immuno-modulation On Traumatic Rats, Brain Research, 2009, 1255:162-9
3.J Wang, J Sun, J Yu, XD Cao, YQ Wang, GC Wu. Sympathetic nervous system mediates surgical trauma stress-induced splenocyte apoptosis in rats, European Journal of Pharmacology, 2007, 565:76–82
4. Zhao, H, Law PY, Loh, HH: Chronic opioid agonist-induced adenylyl cyclase superactivation is dependent on receptor localized within lipid rafts and is independent on receptor internalization. Mol. Pharmacol. 2006, 69: 1421-1432
5. Wang J, Wang YQ, Yu J, Cao XD, Wu GC. Electroacupuncture suppresses surgical trauma stress-induced lymphocyte apoptosis in rats. Neuroscience letters. 2005, Jul 8, 383(1-2): 68-72.
6. Wang J, Jiang JW, Cai SJ, Peng HT, Gao YQ, Cao XD, Wu GC. Effects of electroacupuncture on peripheral T-lymphocyte subsets and proliferation in patients with gastrointestinal tumor treated with surgery and chemotherapy. Shanghai journal of acupuncture and moxibustion. 2004, 23(11): 5-8(In Chinese).
7. Wang J, Jiang JW, Cao XD, Wu GC. Effect of astragalus injection and electroacupuncture on cellular immune function in tramatic stressed rats. Chinese Journal of Integrated traditional and Western Medicine. 2003,23 (Sup): 156-160(In Chinese).
8. Ying-Su Huang, Jian-Wei Jiang, Xiao-Ding Cao & Gen-Cheng Wu. Melatonin enhances lymphocyte proliferation and decreases the release of pituitary pro-opiomelanocortin-derived peptides in surgically tramatized rats. Neuroscience Letters., 343, 109-112, 2003
9. Zhao, H, Du, LN, Jiang, JW, Wu,GC, Cao XD: Neuroimmunal regulation of EA on the traumatic rats. Acupuncture & Electro-Therapeutics Res. INJ. 2002, 27(1): 15-27.
10. Zhao, H, Wu, GC, Cao, XD: Immunomodulatory activity of orphanin FQ/nociceptin on the traumatic rats. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2002 , 23:343-8.
11. Zhao, H, Huang, HW, Wu, GC, Cao, XD: Effect of orphanin FQ on the rat interleukin-1 beta transcripts in the CNS. Neuroscience 2002, 114: 1109-1131.
